MQTT Broadcasting¶
MQTT From http://mqtt.org/:

“MQTT is a machine-to-machine (M2M)/”Internet of Things” connectivity protocol. It was designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport. It is useful for connections with remote locations where a small code footprint is required and/or network bandwidth is at a premium. For example, it has been used in sensors communicating to a broker via satellite link, over occasional dial-up connections with healthcare providers, and in a range of home automation and small device scenarios. It is also ideal for mobile applications because of its small size, low power usage, minimised data packets, and efficient distribution of information to one or many receivers (more http://mqtt.org/faq>)“
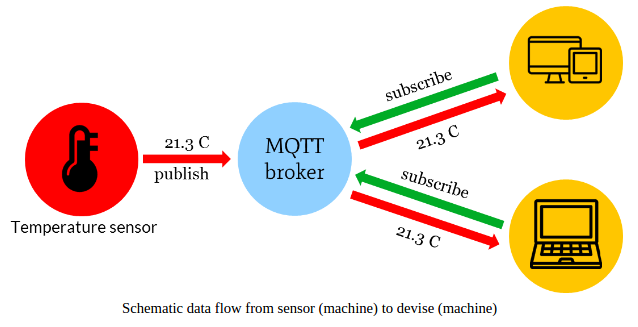
MQTT and istSOS¶
Warning
THIS FEATURE IS STILL EXPERIMENTAL - WE ARE WORKING HARD TO RELEASE SOON A STABLE VERSION - MORE TESTING IS REQUIRED (AND YOU ARE WELCOME TO CONTRIBUTE WITH BUG REPORTING)
Since version 2.3.2 istSOS support MQTT, and specifically can:
- Receive observations from a MQTT broker (instead of using a insertObservation, published data are stored in istSOS and available to SOS clients)
- Publish received observations to a MQTT broker (when a insertObservation is received and the data is stored they are automatically broadcasted to the MQTT broker)

Enabling MQTT broadcasting in istSOS¶
Install the Paho client
This feature require a MQTT python library. In this example we will use the Paho Python Client (https://eclipse.org/paho/clients/python), but istSOS has also been tested with HBMQTT (http://hbmqtt.readthedocs.io/en/latest).
To install the Paho Python Client run:
sudo pip install paho-mqtt
Enable measurements broadcasting
To enable measurements broadcasting go to the “MQTT Publisher” page and register to a MQTT Broker. In this tutorial we will use the Open Source MQTT broker Mosquitto (http://mosquitto.org) available online for testing.
MQTT Broker: =========== ================= URL: iot.eclipse.org Port: 1883 Topic Base: foss4g2016/ =========== =================
Now you can now observe in realtime all the new observations by opening this example html page: http://istsos.org/mqtt/index.html?topic=foss4g2016
This is what you should see:

Enabling MQTT harvesting in istSOS
